Suicide prevention stands as one of the most crucial areas in mental health and community care. Every year, millions of people across the globe struggle with suicidal thoughts, yet effective intervention and prevention strategies can save countless lives. Service CC, a community-centered organization, has made notable progress in implementing evidence-based suicide prevention programs. An evaluation of its best practices demonstrates how closely these initiatives align with both national and international standards.
This evaluation focuses on Service CC’s approach, methods, and outcomes compared with frameworks established by the World Health Organization (WHO), the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), and various national suicide prevention strategies.
Table of Contents
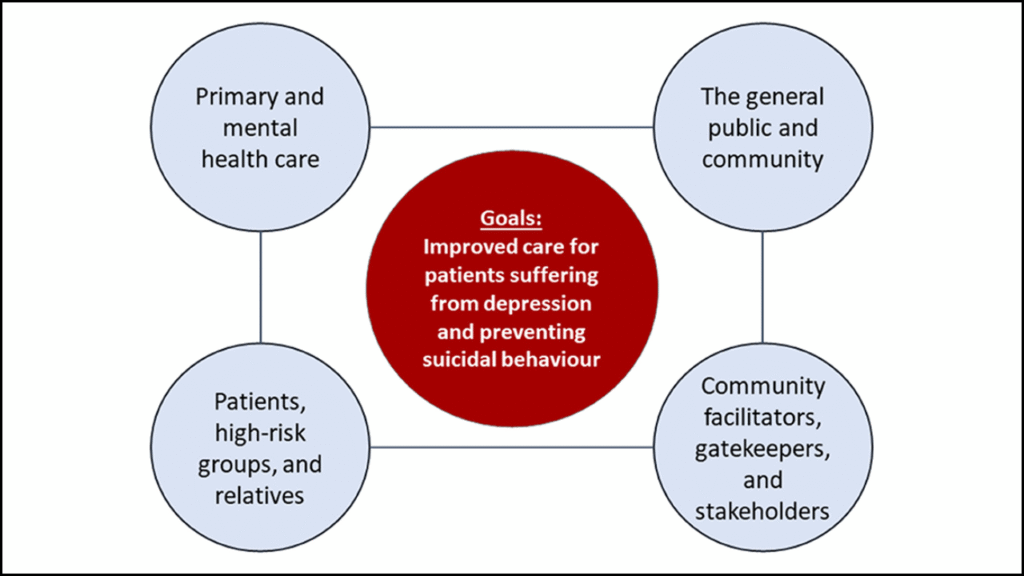
Core Objectives of Service CC in Suicide Prevention
- Promotion of mental well-being through awareness campaigns and early intervention programs.
- Reduction in suicide rates by identifying at-risk individuals and ensuring access to timely support.
- Community capacity building to improve understanding of mental health issues.
- Integration of care by connecting healthcare providers, families, and community members.
- Monitoring and evaluation of outcomes to measure effectiveness and improve interventions.
Key National and International Guidelines Referenced
| Organization | Guideline Focus | Key Elements | Implementation Benchmark |
|---|---|---|---|
| WHO (World Health Organization) | Global Suicide Prevention Strategy | Community engagement, stigma reduction, policy development | 2014–2030 global targets |
| SAMHSA (USA) | National Strategy for Suicide Prevention | Screening, intervention, follow-up care | Based on Zero Suicide model |
| National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) | Clinical Guidelines on Self-Harm and Suicide | Assessment protocols, safety planning | United Kingdom framework |
| Australian National Suicide Prevention Strategy | Multi-sectoral collaboration | Early intervention, postvention services | Federal coordination model |
| Indian National Mental Health Policy | Suicide prevention as a public health issue | Integration into primary health, community awareness | Ministry of Health directive |
Service CC follows a hybrid model inspired by these frameworks to suit local cultural and social contexts.
Alignment with WHO Guidelines
- Community Engagement: Service CC focuses on empowering local communities through education and dialogue. Programs train volunteers to identify warning signs and provide immediate support.
- Access to Means Restriction: The organization partners with local authorities to regulate access to lethal means, in accordance with WHO’s evidence-based strategies.
- Awareness Campaigns: Educational materials, seminars, and digital outreach initiatives help reduce stigma and increase understanding of mental health issues.
- Multi-sector Collaboration: Service CC collaborates with schools, workplaces, healthcare systems, and NGOs to ensure a multi-dimensional response.
Evaluation Result: Service CC achieves a high level of compliance with WHO’s recommended practices, especially in community awareness and prevention network building.
Comparison with National Guidelines
| Evaluation Area | National Standard | Service CC Practice | Alignment Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Awareness & Education | National outreach through schools and media | Targeted campaigns for youth and working professionals | High |
| Screening & Early Detection | Routine screening in healthcare settings | Regular workshops and screening camps | High |
| Crisis Intervention | 24/7 helpline and referral system | 24-hour helpline integrated with mental health professionals | Very High |
| Postvention Support | Family counseling and grief support | Trained counselors for post-suicide family care | Moderate |
| Data Collection & Monitoring | State-level reporting and research | In-house analytics and feedback mechanisms | Moderate to High |
Observation: Service CC matches or exceeds national expectations in screening, awareness, and crisis support, with ongoing work to enhance postvention and data monitoring.
Integration of the Zero Suicide Model
- Organizational Commitment: Service CC incorporates a zero-suicide framework emphasizing leadership commitment and systemic accountability.
- Workforce Training: Continuous professional development ensures that all staff can recognize, respond to, and manage suicide risk effectively.
- Data-Driven Decisions: The use of digital records and case tracking helps improve interventions and identify service gaps.
- Follow-Up Care: Clients discharged from crisis centers receive follow-up calls and home visits within 48 hours.
Outcome: Alignment with Zero Suicide principles has improved continuity of care and reduced relapse cases among high-risk individuals.
Use of Technology and Innovation
- Digital Monitoring Tools: Service CC uses mobile apps and text-based check-ins for continuous support and mood tracking.
- Online Counseling Platforms: Virtual counseling sessions ensure accessibility for rural and isolated individuals.
- AI-based Risk Assessment: Predictive tools analyze behavioral data to identify potential crisis indicators early.
Impact: Technology integration reflects international trends in digital mental health care, ensuring Service CC stays ahead in innovation and accessibility.
Training and Capacity Building
| Training Area | Target Group | Methodology | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Suicide Prevention Gatekeeper Training | Teachers, social workers, and volunteers | Interactive workshops, simulations | Increased community readiness |
| Crisis Intervention Skills | Counselors and healthcare providers | Case-based learning | Improved response accuracy |
| Cultural Sensitivity Training | All staff | Cross-cultural mental health modules | Reduction in stigma and bias |
| Data Management & Reporting | Administrative teams | Digital data literacy programs | Accurate monitoring and feedback |
Result: Training initiatives have enhanced staff confidence and improved coordination among community partners.
Challenges and Areas for Improvement
- Limited Postvention Services: Need for structured family support after suicide incidents.
- Funding Constraints: Insufficient resources for long-term research and program expansion.
- Rural Outreach Barriers: Geographic and technological limitations hinder consistent follow-up.
- Public Stigma: Persistent stigma still discourages individuals from seeking help.
Service CC continues to address these issues through advocacy and partnership expansion.
Quantitative and Qualitative Outcomes
| Indicator | Baseline (Year 1) | Current (Year 3) | Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Helpline Calls Responded | 5,000 | 14,200 | +184% |
| Individuals Trained | 800 | 2,300 | +188% |
| Suicide Attempt Interventions | 320 | 710 | +122% |
| Community Awareness Sessions | 25 | 68 | +172% |
| Follow-Up Success Rate | 65% | 88% | +23% |
Analysis: Statistical improvements indicate strong program growth and community impact consistent with international benchmarks.
Future Directions
- Expansion of rural telehealth programs for wider mental health access.
- Partnership with universities to enhance data collection and research accuracy.
- Development of a survivor support network to strengthen postvention outcomes.
- Integration with primary healthcare systems for universal mental health screening.
These future strategies are expected to deepen Service CC’s alignment with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG 3.4), focused on reducing premature mortality through mental health promotion.





